xz 源码阅读 - 1
继续开坑xz。这次看的是https://sourceforge.net/projects/lzmautils/下的文件(不是go语言写的那个)。根据其示例代码,要解压xz程序,入口是“lzma_code”,让我们从这里开始。
先介绍一下背景。要解压xz文件,需要设置一个lzma_stream对象,并将其next_in设置为数据,avail_in设置为数据长度,然后调用lzma_code开始解析。
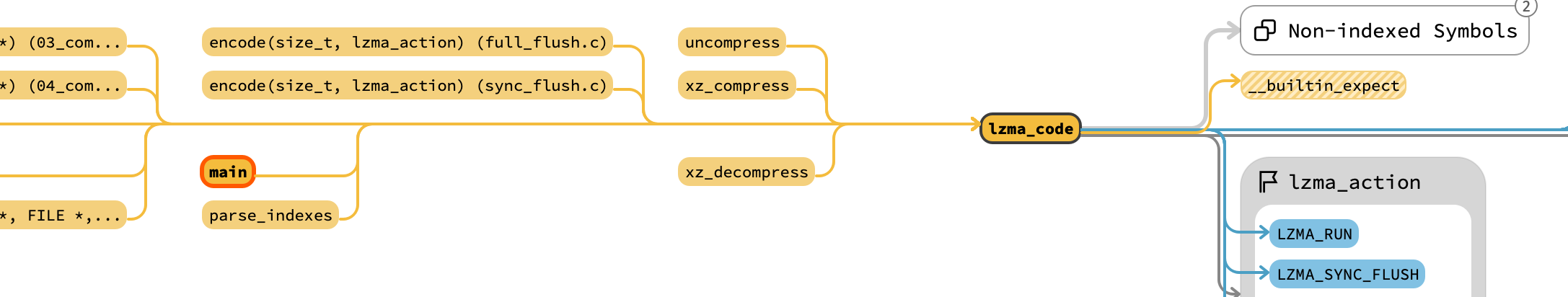
为了举例,先从I:\xz-5.2.5\doc\examples_old\xz_pipe_decomp.c:xz_decompress这个函数看起。
/* note: in_file and out_file must be open already */
int xz_decompress (FILE *in_file, FILE *out_file)
{
lzma_stream strm = LZMA_STREAM_INIT; /* alloc and init lzma_stream struct */
……
/* initialize xz decoder */
ret_xz = lzma_stream_decoder (&strm, memory_limit, flags);
if (ret_xz != LZMA_OK) {
fprintf (stderr, "lzma_stream_decoder error: %d\n", (int) ret_xz);
return RET_ERROR_INIT;
}
lzma_stream_decoder 调用lzma_next_strm_init,
extern LZMA_API(lzma_ret)
lzma_stream_decoder(lzma_stream *strm, uint64_t memlimit, uint32_t flags)
{
lzma_next_strm_init(lzma_stream_decoder_init, strm, memlimit, flags);
strm->internal->supported_actions[LZMA_RUN] = true;
strm->internal->supported_actions[LZMA_FINISH] = true;
return LZMA_OK;
}
对应的,宏定义如下,所以相当于1、lzma_strm_init(strm);;2、lzma_stream_decoder_init(strm->internal->next, strm->allocator, ...args...);。
/// Initializes lzma_strm and calls func() to initialize strm->internal->next.
/// (The function being called will use lzma_next_coder_init()). If
/// initialization fails, memory that wasn't freed by func() is freed
/// along strm->internal.
#define lzma_next_strm_init(func, strm, ...) \
do { \
return_if_error(lzma_strm_init(strm)); \
const lzma_ret ret_ = func(&(strm)->internal->next, \
(strm)->allocator, __VA_ARGS__); \
if (ret_ != LZMA_OK) { \
lzma_end(strm); \
return ret_; \
} \
} while (0)
#endif
调用的lzma_stream_decoder_init如下。
extern lzma_ret
lzma_stream_decoder_init(
lzma_next_coder *next, const lzma_allocator *allocator,
uint64_t memlimit, uint32_t flags)
{
lzma_next_coder_init(&lzma_stream_decoder_init, next, allocator);
if (flags & ~LZMA_SUPPORTED_FLAGS)
return LZMA_OPTIONS_ERROR;
lzma_next_coder_init也是一个宏,它设置next->init,也就是这里的strm->internal->next->init = lzma_stream_decoder_init。
然后下面开始初始化strm->internal->next->coder,并且设置strm->internal->next->code为“stream_decode”等,如代码所示。
lzma_stream_coder *coder = next->coder;
if (coder == NULL) {
coder = lzma_alloc(sizeof(lzma_stream_coder), allocator);
if (coder == NULL)
return LZMA_MEM_ERROR;
next->coder = coder;
next->code = &stream_decode;
next->end = &stream_decoder_end;
next->get_check = &stream_decoder_get_check;
next->memconfig = &stream_decoder_memconfig;
coder->block_decoder = LZMA_NEXT_CODER_INIT;
coder->index_hash = NULL;
}
coder->memlimit = my_max(1, memlimit);
coder->memusage = LZMA_MEMUSAGE_BASE;
coder->tell_no_check = (flags & LZMA_TELL_NO_CHECK) != 0;
coder->tell_unsupported_check
= (flags & LZMA_TELL_UNSUPPORTED_CHECK) != 0;
coder->tell_any_check = (flags & LZMA_TELL_ANY_CHECK) != 0;
coder->ignore_check = (flags & LZMA_IGNORE_CHECK) != 0;
coder->concatenated = (flags & LZMA_CONCATENATED) != 0;
coder->first_stream = true;
return stream_decoder_reset(coder, allocator);
}
回到xz_decompress中。准备好输入数据后,调用lzma_decode。
while ((! in_finished) && (! out_finished)) {
/* read incoming data */
in_len = fread (in_buf, 1, IN_BUF_MAX, in_file);
if (feof (in_file)) {
in_finished = true;
}
if (ferror (in_file)) {
in_finished = true;
ret = RET_ERROR_INPUT;
}
strm.next_in = in_buf;
strm.avail_in = in_len;
/* if no more data from in_buf, flushes the
internal xz buffers and closes the decompressed data
with LZMA_FINISH */
action = in_finished ? LZMA_FINISH : LZMA_RUN;
/* loop until there's no pending decompressed output */
do {
/* out_buf is clean at this point */
strm.next_out = out_buf;
strm.avail_out = OUT_BUF_MAX;
/* decompress data */
ret_xz = lzma_code (&strm, action);
lzma_code的代码截取如下。第一部分是有效性检查,分别检查lzma_stream是否正确设置(internal->next.code需要由其他函数设置成LZMA_NEXT_CODER_INIT)。
extern LZMA_API(lzma_ret)
lzma_code(lzma_stream *strm, lzma_action action)
{
// Sanity checks
if ((strm->next_in == NULL && strm->avail_in != 0)
|| (strm->next_out == NULL && strm->avail_out != 0)
|| strm->internal == NULL
|| strm->internal->next.code == NULL
|| (unsigned int)(action) > LZMA_ACTION_MAX
|| !strm->internal->supported_actions[action])
return LZMA_PROG_ERROR;
// Check if unsupported members have been set to non-zero or non-NULL,
// which would indicate that some new feature is wanted.
if (strm->reserved_ptr1 != NULL
|| strm->reserved_ptr2 != NULL
|| strm->reserved_ptr3 != NULL
|| strm->reserved_ptr4 != NULL
|| strm->reserved_int1 != 0
|| strm->reserved_int2 != 0
|| strm->reserved_int3 != 0
|| strm->reserved_int4 != 0
|| strm->reserved_enum1 != LZMA_RESERVED_ENUM
|| strm->reserved_enum2 != LZMA_RESERVED_ENUM)
return LZMA_OPTIONS_ERROR;
检查通过后,是一个stream中sequence的检查。可以看出来xz由各种状态机组成。这个sequence代表其动作目前的推进状态。
switch (strm->internal->sequence) {
case ISEQ_RUN:
switch (action) {
case LZMA_RUN:
break;
case LZMA_SYNC_FLUSH:
strm->internal->sequence = ISEQ_SYNC_FLUSH;
break;
case LZMA_FULL_FLUSH:
strm->internal->sequence = ISEQ_FULL_FLUSH;
break;
case LZMA_FINISH:
strm->internal->sequence = ISEQ_FINISH;
break;
case LZMA_FULL_BARRIER:
strm->internal->sequence = ISEQ_FULL_BARRIER;
break;
}
break;
case ISEQ_SYNC_FLUSH:
// The same action must be used until we return
// LZMA_STREAM_END, and the amount of input must not change.
if (action != LZMA_SYNC_FLUSH
|| strm->internal->avail_in != strm->avail_in)
return LZMA_PROG_ERROR;
break;
case ISEQ_FULL_FLUSH:
if (action != LZMA_FULL_FLUSH
|| strm->internal->avail_in != strm->avail_in)
return LZMA_PROG_ERROR;
break;
case ISEQ_FINISH:
if (action != LZMA_FINISH
|| strm->internal->avail_in != strm->avail_in)
return LZMA_PROG_ERROR;
break;
case ISEQ_FULL_BARRIER:
if (action != LZMA_FULL_BARRIER
|| strm->internal->avail_in != strm->avail_in)
return LZMA_PROG_ERROR;
break;
case ISEQ_END:
return LZMA_STREAM_END;
case ISEQ_ERROR:
default:
return LZMA_PROG_ERROR;
}
状态操作结束后,调用其next.code()函数来处理。code是一个“lzma_code_function”类型,在每种不同的解码器初始化时,都会初始化自己的结构。
size_t in_pos = 0;
size_t out_pos = 0;
lzma_ret ret = strm->internal->next.code(
strm->internal->next.coder, strm->allocator,
strm->next_in, &in_pos, strm->avail_in,
strm->next_out, &out_pos, strm->avail_out, action);
例如block decoder的:
next->coder = coder;
next->code = &block_decode;
next->end = &block_decoder_end;
coder->next = LZMA_NEXT_CODER_INIT;
index decoder的:
next->coder = coder;
next->code = &index_decode;
next->end = &index_decoder_end;
next->memconfig = &index_decoder_memconfig;
coder->index = NULL;
xz支持的一共有:alone decoder、auto decoder、block decoder、index decoder、stream decoder、delta decoder、lz decoder和它们对应的encoder。xz也支持一个simple decoder,位于simple_coder.c。
以stream_decode为例。进入后,检查coder->sequence。
static lzma_ret
stream_decode(void *coder_ptr, const lzma_allocator *allocator,
const uint8_t *restrict in, size_t *restrict in_pos,
size_t in_size, uint8_t *restrict out,
size_t *restrict out_pos, size_t out_size, lzma_action action)
{
lzma_stream_coder *coder = coder_ptr;
// When decoding the actual Block, it may be able to produce more
// output even if we don't give it any new input.
while (true)
switch (coder->sequence) {
第一步通常是SEQ_STREAM_HEADER。它分别:
case SEQ_STREAM_HEADER: {
// Copy the Stream Header to the internal buffer.
lzma_bufcpy(in, in_pos, in_size, coder->buffer, &coder->pos,
LZMA_STREAM_HEADER_SIZE);
调用lzma_bufcpy拷贝LZMA_STREAM_HEADER_SIZE(12)字节的内容到coder->buffer中。lzma_bufcpy的参数含义是(in, in_pos, in_size, out, out_pos, out_size)。但是在拷贝前会检查源和目标剩余空间(in_avail, out_avail)是否够用。如果长度不够则退出。
// Return if we didn't get the whole Stream Header yet. if (coder->pos < LZMA_STREAM_HEADER_SIZE) return LZMA_OK; coder->pos = 0;解码头部信息。
// Decode the Stream Header. const lzma_ret ret = lzma_stream_header_decode( &coder->stream_flags, coder->buffer); if (ret != LZMA_OK) return ret == LZMA_FORMAT_ERROR && !coder->first_stream ? LZMA_DATA_ERROR : ret;
lzma_stream_header_decode的代码如下:
extern LZMA_API(lzma_ret)
lzma_stream_header_decode(lzma_stream_flags *options, const uint8_t *in)
{
-- 2.1 比较magic
// Magic
if (memcmp(in, lzma_header_magic, sizeof(lzma_header_magic)) != 0)
return LZMA_FORMAT_ERROR;
-- 2.2 比较in + 6的2字节CRC值和in + 6 + 2处保存的是否一致。
// Verify the CRC32 so we can distinguish between corrupt
// and unsupported files.
const uint32_t crc = lzma_crc32(in + sizeof(lzma_header_magic),
LZMA_STREAM_FLAGS_SIZE, 0);
if (crc != read32le(in + sizeof(lzma_header_magic)
+ LZMA_STREAM_FLAGS_SIZE))
return LZMA_DATA_ERROR;
-- 2.3 解码flags。其实只用来确定options->check = in1 & 0x0f。
// Stream Flags
if (stream_flags_decode(options, in + sizeof(lzma_header_magic)))
return LZMA_OPTIONS_ERROR;
// Set Backward Size to indicate unknown value. That way
// lzma_stream_flags_compare() can be used to compare Stream Header
// and Stream Footer while keeping it useful also for comparing
// two Stream Footers.
options->backward_size = LZMA_VLI_UNKNOWN;
return LZMA_OK;
}
拷贝刚才获取到的options->check,并进入下一个sequence。
// If we are decoding concatenated Streams, and the later // Streams have invalid Header Magic Bytes, we give // LZMA_DATA_ERROR instead of LZMA_FORMAT_ERROR. coder->first_stream = false; // Copy the type of the Check so that Block Header and Block // decoders see it. coder->block_options.check = coder->stream_flags.check; // Even if we return LZMA_*_CHECK below, we want // to continue from Block Header decoding. coder->sequence = SEQ_BLOCK_HEADER; // Detect if there's no integrity check or if it is // unsupported if those were requested by the application. if (coder->tell_no_check && coder->stream_flags.check == LZMA_CHECK_NONE) return LZMA_NO_CHECK; if (coder->tell_unsupported_check && !lzma_check_is_supported( coder->stream_flags.check)) return LZMA_UNSUPPORTED_CHECK; if (coder->tell_any_check) return LZMA_GET_CHECK;}
两个sequence中间没有break,所以直接进入。这里我们也重新计数。
如果in[*in_pos]为0,则退出当前处理,设置sequence为SEQ_INDEX。如果不是则调用lzma_block_header_size_decode宏进行处理。值为 (x + 1) * 4 。
// Fall through
case SEQ_BLOCK_HEADER: {
if (*in_pos >= in_size)
return LZMA_OK;if (coder->pos == 0) { // Detect if it's Index. if (in[*in_pos] == 0x00) { coder->sequence = SEQ_INDEX; break; } // Calculate the size of the Block Header. Note that // Block Header decoder wants to see this byte too // so don't advance *in_pos. coder->block_options.header_size = lzma_block_header_size_decode( in[*in_pos]); }拷贝声明的header_size到code->buffer中。
// Copy the Block Header to the internal buffer. lzma_bufcpy(in, in_pos, in_size, coder->buffer, &coder->pos, coder->block_options.header_size); // Return if we didn't get the whole Block Header yet. if (coder->pos < coder->block_options.header_size) return LZMA_OK; coder->pos = 0; // Version 1 is needed to support the .ignore_check option. coder->block_options.version = 1;设置一个长度为LZMA_FILTERS_MAX + 1(4 + 1)的filters buffer。调用lzma_block_header_decoder解析头信息。
// Set up a buffer to hold the filter chain. Block Header // decoder will initialize all members of this array so // we don't need to do it here. lzma_filter filters[LZMA_FILTERS_MAX + 1]; coder->block_options.filters = filters; // Decode the Block Header. return_if_error(lzma_block_header_decode(&coder->block_options, allocator, coder->buffer));
3.1 lzma_block_header_decoder的定义如下。初始化所有的filters。
extern LZMA_API(lzma_ret)
lzma_block_header_decode(lzma_block *block,
const lzma_allocator *allocator, const uint8_t *in)
{
// NOTE: We consider the header to be corrupt not only when the
// CRC32 doesn't match, but also when variable-length integers
// are invalid or over 63 bits, or if the header is too small
// to contain the claimed information.
// Initialize the filter options array. This way the caller can
// safely free() the options even if an error occurs in this function.
for (size_t i = 0; i <= LZMA_FILTERS_MAX; ++i) {
block->filters[i].id = LZMA_VLI_UNKNOWN;
block->filters[i].options = NULL;
}
// Versions 0 and 1 are supported. If a newer version was specified,
// we need to downgrade it.
if (block->version > 1)
block->version = 1;
// This isn't a Block Header option, but since the decompressor will
// read it if version >= 1, it's better to initialize it here than
// to expect the caller to do it since in almost all cases this
// should be false.
block->ignore_check = false;
3.2 调用lzma_block_header_size_decode宏(复习一下, (x+1) * 4)来对比数据。并校验节的crc32。
// Validate Block Header Size and Check type. The caller must have
// already set these, so it is a programming error if this test fails.
if (lzma_block_header_size_decode(in[0]) != block->header_size
|| (unsigned int)(block->check) > LZMA_CHECK_ID_MAX)
return LZMA_PROG_ERROR;
// Exclude the CRC32 field.
const size_t in_size = block->header_size - 4;
// Verify CRC32
if (lzma_crc32(in, in_size, 0) != read32le(in + in_size))
return LZMA_DATA_ERROR;
// Check for unsupported flags.
if (in[1] & 0x3C)
return LZMA_OPTIONS_ERROR;
// Start after the Block Header Size and Block Flags fields.
size_t in_pos = 2;
3.3 这里出现了一个lzma_vli_decode函数。vli代表“variable length integer”。变长整数的范围是0~ 0x7fffffff`ffffffff,最长耗费9字节。lzma_vli_decode(vli, vli_pos, in, in_pos, in_size)会做一些校验,并正确实现转换。
因此这里获取“compressed_size”,是压缩后的大小,并校验是否对齐以及是否过长。当然如代码所示,也可以是未知大小。
// Compressed Size
if (in[1] & 0x40) {
return_if_error(lzma_vli_decode(&block->compressed_size,
NULL, in, &in_pos, in_size));
// Validate Compressed Size. This checks that it isn't zero
// and that the total size of the Block is a valid VLI.
if (lzma_block_unpadded_size(block) == 0)
return LZMA_DATA_ERROR;
} else {
block->compressed_size = LZMA_VLI_UNKNOWN;
}
3.4 同样的,获取解压后的大小。
// Uncompressed Size
if (in[1] & 0x80)
return_if_error(lzma_vli_decode(&block->uncompressed_size,
NULL, in, &in_pos, in_size));
else
block->uncompressed_size = LZMA_VLI_UNKNOWN;
3.5 接下来处理各种filter。最多可以有4个。
// Filter Flags
const size_t filter_count = (in[1] & 3U) + 1;
for (size_t i = 0; i < filter_count; ++i) {
const lzma_ret ret = lzma_filter_flags_decode(
&block->filters[i], allocator,
in, &in_pos, in_size);
if (ret != LZMA_OK) {
free_properties(block, allocator);
return ret;
}
}
3.5.1 lzma_filter_flags_decode稍微麻烦点,贴一下代码看看。首先,解码filter id。id最大序号是1 << 62 - 1。 然后,解码property size。property size最大不能超过剩余长度。然后调用lzma_properties_decode进一步解析属性。
extern LZMA_API(lzma_ret)
lzma_filter_flags_decode(
lzma_filter *filter, const lzma_allocator *allocator,
const uint8_t *in, size_t *in_pos, size_t in_size)
{
// Set the pointer to NULL so the caller can always safely free it.
filter->options = NULL;
// Filter ID
return_if_error(lzma_vli_decode(&filter->id, NULL,
in, in_pos, in_size));
if (filter->id >= LZMA_FILTER_RESERVED_START)
return LZMA_DATA_ERROR;
// Size of Properties
lzma_vli props_size;
return_if_error(lzma_vli_decode(&props_size, NULL,
in, in_pos, in_size));
// Filter Properties
if (in_size - *in_pos < props_size)
return LZMA_DATA_ERROR;
const lzma_ret ret = lzma_properties_decode(
filter, allocator, in + *in_pos, props_size);
*in_pos += props_size;
return ret;
}
3.5.2 lzma_properties_decode代码如下。对filter->id搜索合适的decoder。根据xz的配置可以有不同的decoder,Linux中的liblzma.so.5.2.4支持全部9种decoder,逆向结果如下(代码被高度优化,但结果就是会遍历9项,而decoder最多也支持9种)。
每个decoder由四个段组成,分别是{.id = xx, .init = 初始化函数, .memusage = null 或者对应函数, .props_decode = props_decode函数(通常都是lzma_simple_props_decode,少数不同)}。
__int64 __fastcall lzma_properties_decode(_QWORD *a1, __int64 a2, __int64 a3, __int64 a4)
{
……
a1[1] = 0LL;
v4 = 0LL;
for ( i = 0x4000000000000001LL; *a1 != i; i = *((_QWORD *)&unk_26CC0 + 4 * v4) )
{
if ( ++v4 == 9 )
return 8LL;
}
……
}
extern LZMA_API(lzma_ret)
lzma_properties_decode(lzma_filter *filter, const lzma_allocator *allocator,
const uint8_t *props, size_t props_size)
{
// Make it always NULL so that the caller can always safely free() it.
filter->options = NULL;
const lzma_filter_decoder *const fd = decoder_find(filter->id);
if (fd == NULL)
return LZMA_OPTIONS_ERROR;
if (fd->props_decode == NULL)
return props_size == 0 ? LZMA_OK : LZMA_OPTIONS_ERROR;
最后调用对应的props_decode函数。
return fd->props_decode(
&filter->options, allocator, props, props_size);
}
3.5.2.1 为了方便后续理解,这里把三种都读一遍。第一个是lzma_lzma_props_decode。要求prop_size为5,
extern lzma_ret
lzma_lzma_props_decode(void **options, const lzma_allocator *allocator,
const uint8_t *props, size_t props_size)
{
if (props_size != 5)
return LZMA_OPTIONS_ERROR;
lzma_options_lzma *opt
= lzma_alloc(sizeof(lzma_options_lzma), allocator);
if (opt == NULL)
return LZMA_MEM_ERROR;
3.5.2.2 调用lzma_lzma_lclppb_decode。字节最多不超过24*9+8=224。然后设置pb/lp/lc,说是要看规范,这里先不管了。
if (lzma_lzma_lclppb_decode(opt, props[0]))
goto error;
extern bool
lzma_lzma_lclppb_decode(lzma_options_lzma *options, uint8_t byte)
{
if (byte > (4 * 5 + 4) * 9 + 8)
return true;
// See the file format specification to understand this.
options->pb = byte / (9 * 5);
byte -= options->pb * 9 * 5;
options->lp = byte / 9;
options->lc = byte - options->lp * 9;
return options->lc + options->lp > LZMA_LCLP_MAX;
}
3.5.2.3 接下来看另一个,lzma_lzma2_props_decode。要求prop_size为1,该属性决定其字典大小。
extern lzma_ret
lzma_lzma2_props_decode(void **options, const lzma_allocator *allocator,
const uint8_t *props, size_t props_size)
{
if (props_size != 1)
return LZMA_OPTIONS_ERROR;
// Check that reserved bits are unset.
if (props[0] & 0xC0)
return LZMA_OPTIONS_ERROR;
// Decode the dictionary size.
if (props[0] > 40)
return LZMA_OPTIONS_ERROR;
lzma_options_lzma *opt = lzma_alloc(
sizeof(lzma_options_lzma), allocator);
if (opt == NULL)
return LZMA_MEM_ERROR;
if (props[0] == 40) {
opt->dict_size = UINT32_MAX;
} else {
opt->dict_size = 2 | (props[0] & 1U);
opt->dict_size <<= props[0] / 2U + 11;
}
opt->preset_dict = NULL;
opt->preset_dict_size = 0;
*options = opt;
return LZMA_OK;
}
3.5.2.4 最后是lzma_simple_props_decode。大小可以为0~4字节。可以用来设置start_offset。
extern lzma_ret
lzma_simple_props_decode(void **options, const lzma_allocator *allocator,
const uint8_t *props, size_t props_size)
{
if (props_size == 0)
return LZMA_OK;
if (props_size != 4)
return LZMA_OPTIONS_ERROR;
lzma_options_bcj *opt = lzma_alloc(
sizeof(lzma_options_bcj), allocator);
if (opt == NULL)
return LZMA_MEM_ERROR;
opt->start_offset = read32le(props);
// Don't leave an options structure allocated if start_offset is zero.
if (opt->start_offset == 0)
lzma_free(opt, allocator);
else
*options = opt;
return LZMA_OK;
}
3.5.2.5 回到上层lzma_lzma_props_decode中,设置dict_size,函数退出。
// All dictionary sizes are accepted, including zero. LZ decoder
// will automatically use a dictionary at least a few KiB even if
// a smaller dictionary is requested.
opt->dict_size = read32le(props + 1);
opt->preset_dict = NULL;
opt->preset_dict_size = 0;
*options = opt;
return LZMA_OK;
error:
lzma_free(opt, allocator);
return LZMA_OPTIONS_ERROR;
}
3.5.3 处理剩余padding部分
// Padding
while (in_pos < in_size) {
if (in[in_pos++] != 0x00) {
free_properties(block, allocator);
// Possibly some new field present so use
// LZMA_OPTIONS_ERROR instead of LZMA_DATA_ERROR.
return LZMA_OPTIONS_ERROR;
}
}
return LZMA_OK;
}
3.6 终于返回最外层,stream_decode里面。循环遍历,如果有内存消耗计算器则调用并添加,如果没有则用1024近似替代。其实memusage函数也很简单,就是统计结构体+字典的内存占用。
// If LZMA_IGNORE_CHECK was used, this flag needs to be set.
// It has to be set after lzma_block_header_decode() because
// it always resets this to false.
coder->block_options.ignore_check = coder->ignore_check;
// Check the memory usage limit.
const uint64_t memusage = lzma_raw_decoder_memusage(filters);
lzma_ret ret;
extern uint64_t
lzma_lz_decoder_memusage(size_t dictionary_size)
{
return sizeof(lzma_coder) + (uint64_t)(dictionary_size);
}
3.7 这个主要为了避免字典过大(超过coder->memlimit)。如果一切ok,则调用lzma_block_decoder_init。
if (memusage == UINT64_MAX) {
// One or more unknown Filter IDs.
ret = LZMA_OPTIONS_ERROR;
} else {
// Now we can set coder->memusage since we know that
// the filter chain is valid. We don't want
// lzma_memusage() to return UINT64_MAX in case of
// invalid filter chain.
coder->memusage = memusage;
if (memusage > coder->memlimit) {
// The chain would need too much memory.
ret = LZMA_MEMLIMIT_ERROR;
} else {
// Memory usage is OK.
// Initialize the Block decoder.
ret = lzma_block_decoder_init(
&coder->block_decoder,
allocator,
&coder->block_options);
}
}
3.7.1 lzma_block_decoder_init调用lzma_next_code_init来设置next->init为lzma_block_decoder_init。然后对数据进行校验。这个函数和最上面介绍的lzma_stream_decoder_init其实很像。
extern lzma_ret
lzma_block_decoder_init(lzma_next_coder *next, const lzma_allocator *allocator,
lzma_block *block)
{
lzma_next_coder_init(&lzma_block_decoder_init, next, allocator);
// Validate the options. lzma_block_unpadded_size() does that for us
// except for Uncompressed Size and filters. Filters are validated
// by the raw decoder.
if (lzma_block_unpadded_size(block) == 0
|| !lzma_vli_is_valid(block->uncompressed_size))
return LZMA_PROG_ERROR;
3.7.2 如果没有next->coder则初始化它。code设置为block_decode。然后进行其他的初始化。
// Allocate *next->coder if needed.
lzma_block_coder *coder = next->coder;
if (coder == NULL) {
coder = lzma_alloc(sizeof(lzma_block_coder), allocator);
if (coder == NULL)
return LZMA_MEM_ERROR;
next->coder = coder;
next->code = &block_decode;
next->end = &block_decoder_end;
coder->next = LZMA_NEXT_CODER_INIT;
}
// Basic initializations
coder->sequence = SEQ_CODE;
coder->block = block;
coder->compressed_size = 0;
coder->uncompressed_size = 0;
// If Compressed Size is not known, we calculate the maximum allowed
// value so that encoded size of the Block (including Block Padding)
// is still a valid VLI and a multiple of four.
coder->compressed_limit
= block->compressed_size == LZMA_VLI_UNKNOWN
? (LZMA_VLI_MAX & ~LZMA_VLI_C(3))
- block->header_size
- lzma_check_size(block->check)
: block->compressed_size;
3.7.3 最后一部分是对lzma_check_init的调用,其实就是初始化crc32/64对应的字段为0。然后循环调用lzma_raw_decoder_init,直到所有的filter都处理完成。
// Initialize the check. It's caller's problem if the Check ID is not
// supported, and the Block decoder cannot verify the Check field.
// Caller can test lzma_check_is_supported(block->check).
coder->check_pos = 0;
lzma_check_init(&coder->check, block->check);
coder->ignore_check = block->version >= 1
? block->ignore_check : false;
// Initialize the filter chain.
return lzma_raw_decoder_init(&coder->next, allocator,
block->filters);
}
3.8 回到外层。清理之前的临时filters对象。并设置序列状态为SEQ_BLOCK。
// Free the allocated filter options since they are needed
// only to initialize the Block decoder.
for (size_t i = 0; i < LZMA_FILTERS_MAX; ++i)
lzma_free(filters[i].options, allocator);
coder->block_options.filters = NULL;
// Check if memory usage calculation and Block enocoder
// initialization succeeded.
if (ret != LZMA_OK)
return ret;
coder->sequence = SEQ_BLOCK;
}
这一节太长了,开一个新文章继续。